
Gelatin is particularly rich in glycine, proline, and lysine, which are essential for collagen synthesis.īonus: Gelatin may boost gut health and lower inflammation. Gelatin is packed with the amino acids necessary for collagen production, which provides structure and support for your skin. A 2009 study showed that gelatin supplementation was more effective for reducing appetite than supplementation with casein, a protein found in milk. A 2008 study in people with obesity found that supplementing with gelatin increased the appetite-reducing hormone glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). One study with rats suggested that gelatin may help enhance insulin secretion and improve glycemic control. A review of studies showed that you’ll need extra protein for specific amino acids like glycine and arginine, so adding gelatin or collagen supplements may be helpful. Gelatin is packed with amino acids that support your body during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Helpful during pregnancy and breastfeeding.Better collagen production is good news for your joints, which depend on a collagen-rich network to provide their structure. One study suggested that supplementing with collagen may help improve collagen production. Here are a few gelatin benefits that have science on their side: Gelatin and collagen contain the same amino acids in similar amounts, so their benefits overlap. Note: Use this as a base recipe and change it up based on the fruit and fruit juice you have on hand.Gelatin supplements have been linked to some awesome health benefits. Pour over the sliced cherries and cover.In a separate bowl, add the cherry juice and whisk in 2 tablespoons of the gelatin-water mixture. Place the sliced cherries in the bottom of a glass bowl.In a small saucepan, bring the water to a boil over high heat.And hey, if you want the benefits of gelatin, and still want to enjoy that sweet treat from your childhood? Make your own Jell-O: it’s easy! Here’s how: Healthy Cherry Gelatin Because our diets often lack natural forms of gelatin, supplementation may be a good idea. Gelatin can also be taken as a supplement. Gelatin powder can even be used to make an egg substitute for baking: simply mix 1 tablespoon gelatin with 3 tablespoons water. Try adding gelatin powder to water and drinking right before bed to help you sleep. You can also buy gelatin powder and use it as a thickening agent in recipes, mix it in hot drinks, or add it to smoothies. Once you have some on hand, use in any recipe that calls for stock, use it to make a stew, or simply drink it.
One way to consume gelatin is by making your own bone broth. Improved gut health: The glutamic acid in gelatin may help repair and protect the gut wall from damage, helping to prevent “leaky gut,” a condition where potentially harmful substances can pass through the gut into the bloodstream.Improved brain health: The high amounts of glycine in gelatin may improve memory and attention.Injury prevention: Adding gelatin to an intermittent exercise program improves collagen synthesis and could play a role in injury prevention and tissue repair.Improved bone and joint health: Although there is insufficient evidence for treating osteoarthritis with gelatin, recent studies have shown a significant reduction in joint pain compared to a placebo.Thicker hair: Multiple studies have shown increased hair numbers and individual hair thickness with gelatin supplements.

Better skin: Gelatin has been shown to increase moisture levels and collagen density in the skin.Improved sleep: Gelatin is the richest food source of the amino acid glycine which has been shown to improve sleep quality when taken right before bed.What Are Some of the Health Benefits of Gelatin? And since we don’t typically eat collagenous joints, tendons and connective tissue, supplementing with gelatin can be one good way to get those essential amino acids into our diet. While our bodies make some amino acids, we need to get the rest through our diet.

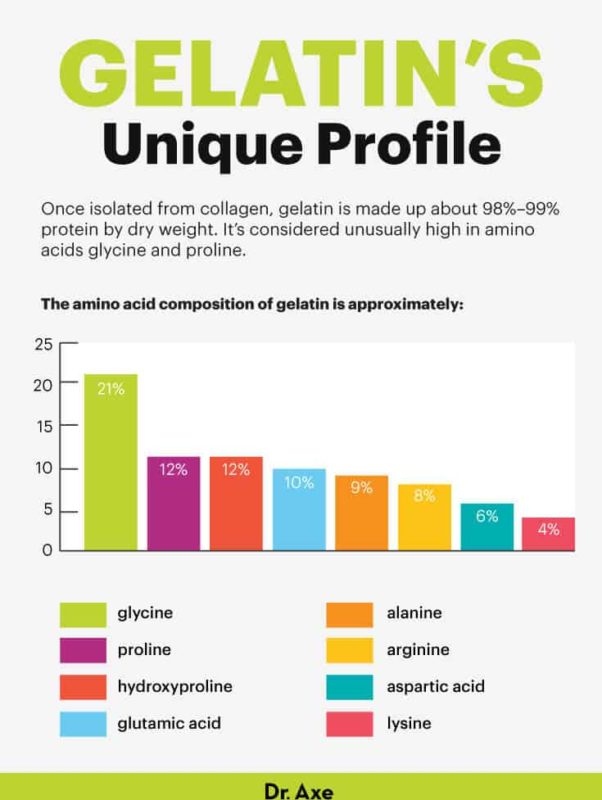
The most abundant amino acids in gelatin are glycine, proline, valine, hydroxyproline and glutamic acid. Gelatin is made almost entirely of protein and has a unique amino acid profile, giving its many health benefits. Flavorless and colorless, gelatin dissolves in warm liquids and gels as it cools.

Gelatin is a powder made from the collagenous joints, tendons, and connective tissues of animals, typically cows, pigs and sometimes fish. Although you don’t see as much Jell-O these days, quality-sourced gelatin is quickly rising in popularity thanks to its many potential health benefits. The silky sweet treat was a staple of my childhood and always a hit at holiday parties. When you hear the word gelatin, what comes to mind first? Jell-O? Yep, me too.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
